Every great product begins as a concept, but it can only become a reality with the proper tooling. A product must undergo testing, improvement, and validation before going into mass production. Prototyping tooling can help with it. The process of developing temporary or semi-production tools to produce sample parts for assessment is known as prototype tooling. Automotive, consumer electronics, medical gadgets, industrial equipment, and packaging are just a few of the industries that utilize it extensively. Read till the end to learn how concepts become tangible products.
Every product starts with an idea, which is frequently represented by CAD models or drawings. The objective at this point is to specify the functions and appearance of the product. Dimensions, material choice, tolerances, and functional needs are the main concerns of designers.
These digital concepts become tangible through prototype tooling. It enables teams to verify if the design functions in practical settings. Without this stage, a lot of design defects would only show up during full production, and at this point, it would be costly to rectify them.
Engineers design the tooling when the design is complete. This includes making decisions on the construction of the tool, the release of parts, and the flow of materials.
At this point, teams also select tooling materials according to testing requirements and anticipated production volume. Softer steels for longer testing and aluminum for rapid iterations are common choices. Prototype tooling choices frequently ensure a balance between accuracy, cost, and speed.
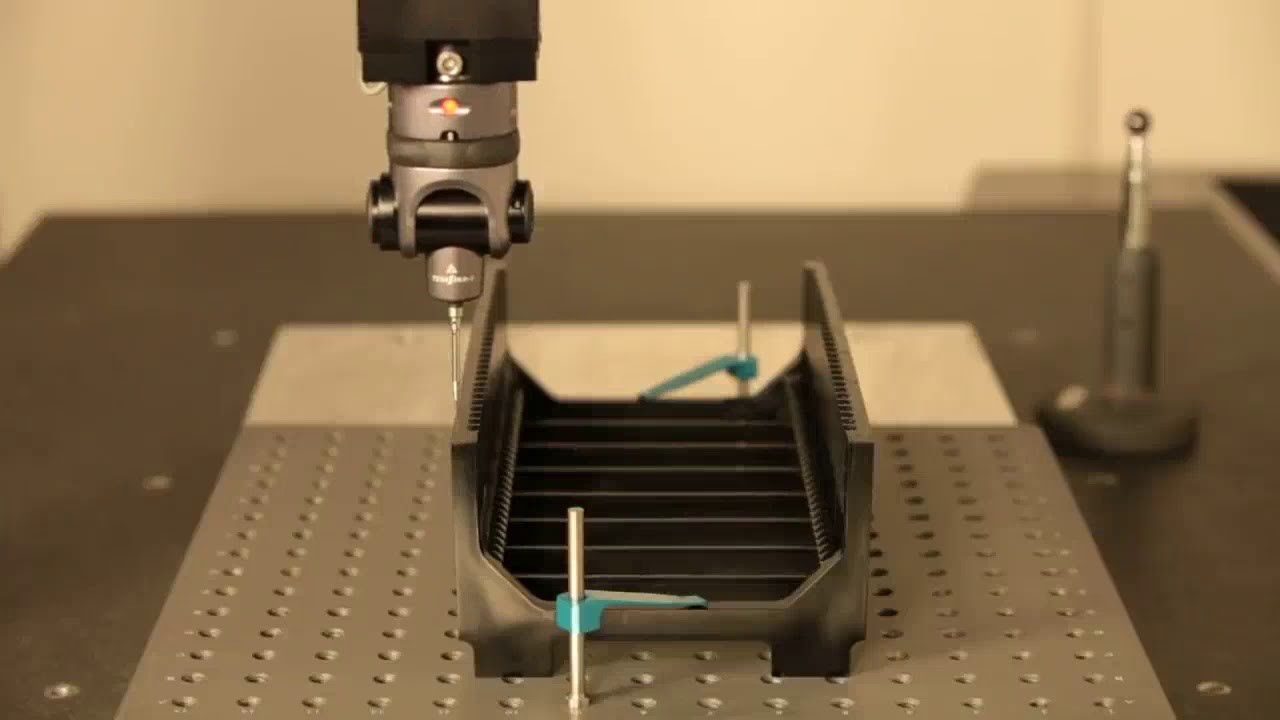
The actual tool is then manufactured using CNC machining or similar processes. Trial runs are carried out to create sample parts after they are prepared. The functional performance, surface quality, and dimensional correctness of these samples are all closely examined.
This is the starting point for actual learning. Teams check the consistency of the pieces and the behavior of the material. Typical checks at this point consist of:
● Accuracy of fit and assembly
● Strength of structure
● Surface quality
● Repeatability in several samples
Trial runs uncover problems that designers cannot foresee.
This might be user feedback sessions, environmental exposure, or mechanical stress testing. Problems found during testing are fed back into the design. The tooling or part design is then modified. Until performance standards are reached, this cycle may be repeated several times. This step is critical as it reduces risks associated with products.
| Feature | 3D Printing | Prototyping Tooling |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Limited Resins | Production-Grade Plastics |
| Functional Testing | Basic/Visual | Full Mechanical Validation |
The project advances to production tooling after the prototype meets all functional and quality criteria. Prototype tooling provides valuable insights that inform final tool design, material selection, and process parameters.
Due to the resolution of doubts, this transition is more seamless. Timelines get better, production quality stabilizes, and costs become predictable.
To put it briefly, prototype tooling makes final production much more reliable by bridging the gap between innovation and manufacturing reality.
Prototyping tooling is useful and crucial from the initial drawing to the final result. Before committing to large-scale manufacturing, it allows teams to test ideas, correct mistakes, and gain confidence. Prototyping tools may reduce costs, save time, and enhance product quality in a variety of sectors when utilised properly. For anyone who is serious about creating dependable products, this is not an optional step but a smart one, particularly when scaling through injection moulding in China.
Ready to move beyond 3D prints? Contact Uttmould today for a free DFM analysis and a prototyping tooling quote tailored to your project’s needs.
What is the purpose of prototyping tooling?
Before purchasing full production tools, prototyping tooling is used to create sample parts for evaluating design, fit, function, and manufacturability.
Which sectors are most reliant on prototyping tooling?
Prototyping tooling is often used in the automotive, medical, consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and packaging sectors during the stages of product development.
What differentiates production tooling from prototype tooling?
Production tooling is made for long-term durability and high-volume manufacturing, whereas prototyping tooling concentrates on testing and iteration.
Does the use of prototyping tools lower development costs?
Yes, it helps in the early detection of design and process issues, avoiding expensive adjustments and production delays.
What is the duration of the tooling prototyping process?
Prototyping tooling usually takes weeks instead of months, allowing for quicker validation and decision-making, while timelines vary depending on complexity.